Latest in research
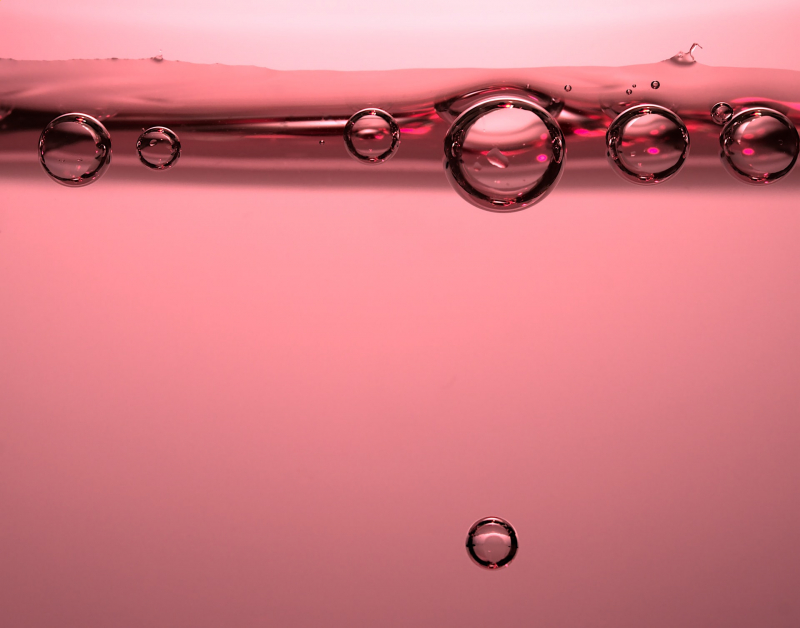
Bubble-reading
Scientists from the Infochemistry Scientific Center have devised a novel way to gauge the concentration of water-alcohol solutions by looking at… bubbles. The team’s neural network is able to assess the behavior and shape of air bubbles in various solutions and accurately identify the ratio of water to alcohol. The study itself was born from an idea put forth by a high school student who has since become an intern at the center. Potential applications include targeted drug delivery and even detection of impurities in natural gas.
Nanodots for medicine
Meanwhile, an international research team that includes scientists from ITMO University has uncovered a new way to synthesize carbon dots with stable optical properties. For reference, these remarkable nanomaterials are low in toxicity, luminescent, and easily controlled. All these qualities make them a perfect fit for a myriad of applications in biology and medicine, including in diagnostics.
Carbon dots at ITMO University's International Research and Educational Center for Physics of Nanostructures. Photo by ITMO.NEWS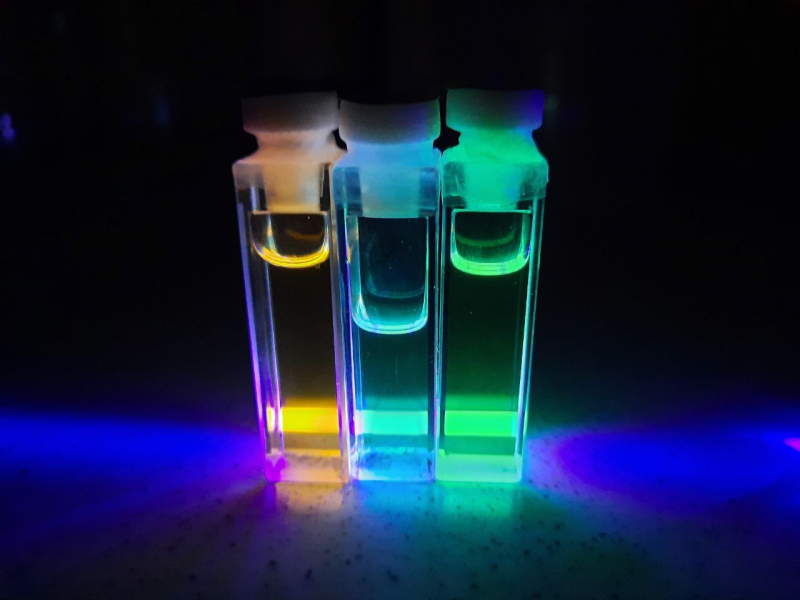
What’s notable about these particular particles is their optical chirality. As the researchers note, their findings may contribute to the development of tools for the detection of DNA defects and oncological diseases, as well as targeted drug delivery.
Elastic wonders
Last but not least, researchers from the ChemBio Cluster have developed miniature elastic robots capable of extracting blood clots from within veins without causing damage to the blood vessels. This highly promising thrombosis treatment has the potential to make surgical intervention much quicker and safer for patients.
A medical robot developed at ITMO University. Credit: Dmitry Grigoryev, ITMO.NEWS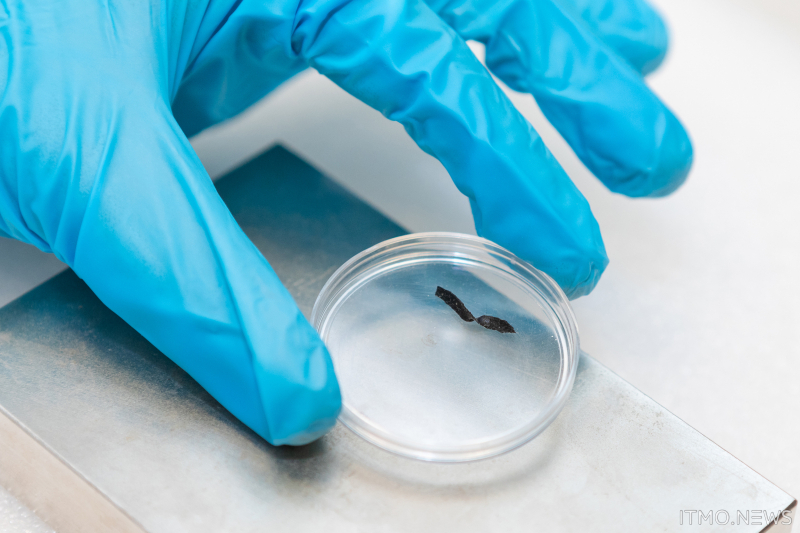
New program: Master’s in industrial AI
Launching in the 2022/2023 academic year, AI in the Industry is a program for future developers of AI-based solutions. Close ties to industrial partners (including oil-and-gas giant Gazprom Neft) guarantee that the students will be able to dive head-on into their chosen field, acquire valuable experience, and lay the groundwork for their professional development.
Gazprom Neft’s Science and Technology Center. Credit: ntc.gazprom-neft.ru