Bachelor (Бакалавр)
The journey through the Russian higher education system typically begins with a Bachelor's degree program, which typically spans four years. Students are exposed to a diverse range of courses that encompass both core and elective subjects. The curriculum emphasizes foundational knowledge and skills crucial to the students’ professional development. Additionally, students may be required to complete internships or practical projects to gain hands-on experience in their chosen field. At the end of the program, students are required to pass comprehensive exams and defend a thesis before graduating with a Bachelor's degree.
Master (Магистр)
After completing their Bachelor's degree, students have the option to pursue a Master's degree, which generally lasts for two years. Such programs provide a more specialized and in-depth exploration of a chosen field. They are designed to prepare students for advanced roles within education, research, and industry. Master's programs place a strong emphasis on research and independent studies. Students are required to complete a thesis or research project that contributes to the overall knowledge in their subject area. Collaborative projects, seminars, and workshops further enhance students' critical thinking and analytical skills.
Learn more about ITMO’s English-taught international Master’s programs here.
Specialist (Специалист)
In addition to Bachelor's and Master's degree programs, the Russian system include Specialist’s programs, which are highly focused and provide intensive training in specialized subjects, such as medicine, law, and engineering. These programs usually last for 5 years.
Candidate of Sciences (Кандидат наук)
This is a research-based academic degree that is equivalent to a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD). It requires the successful completion of original research, defense of a dissertation, and major contributions to the field of knowledge.
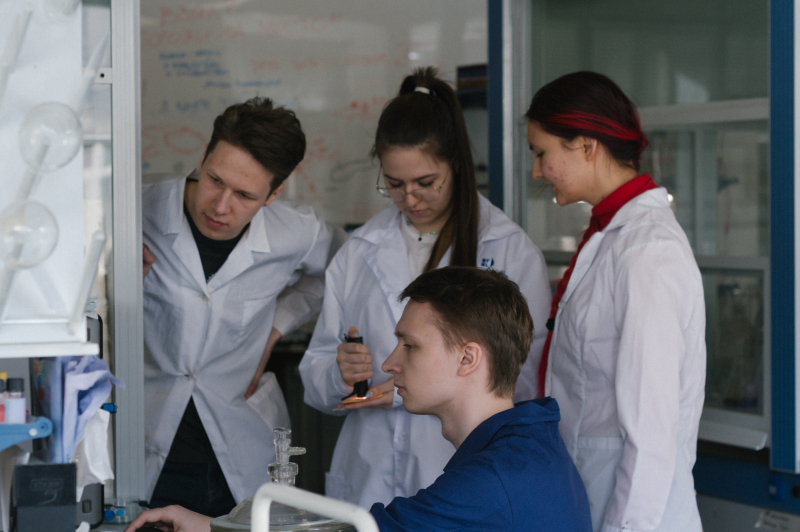

Researchers and students at ITMO. Credit: ITMO.NEWS
Doctor of Sciences (Доктор наук)
This is the highest academic degree in Russia, even higher than a PhD (its closest overseas equivalent is habilitation). It requires extensive original research, a significant body of published work, and a dissertation defense. Additionally, a candidate pursuing a Doctor of Science degree would also be involved in several teaching and administrative duties.
Conclusion
The Russian higher education system stands as a testament to the country's commitment to academic excellence and training of highly-skilled professionals in every scientific field. The system's multi-stage structure ensures that students receive a comprehensive education that blends theoretical knowledge with practical skills. The rigorous admission processes, credit-based academic system, and stringent grading standards reflect Russia's dedication to maintaining high educational standards.
As students progress through the stages of education within the Russian higher education system, they not only gain subject-specific expertise but also develop critical thinking, research, and problem-solving skills that are essential for success in their chosen careers. Whether one aspires to excel in education, research, or industry, the Russian higher education system provides a solid foundation for personal and professional growth.